|
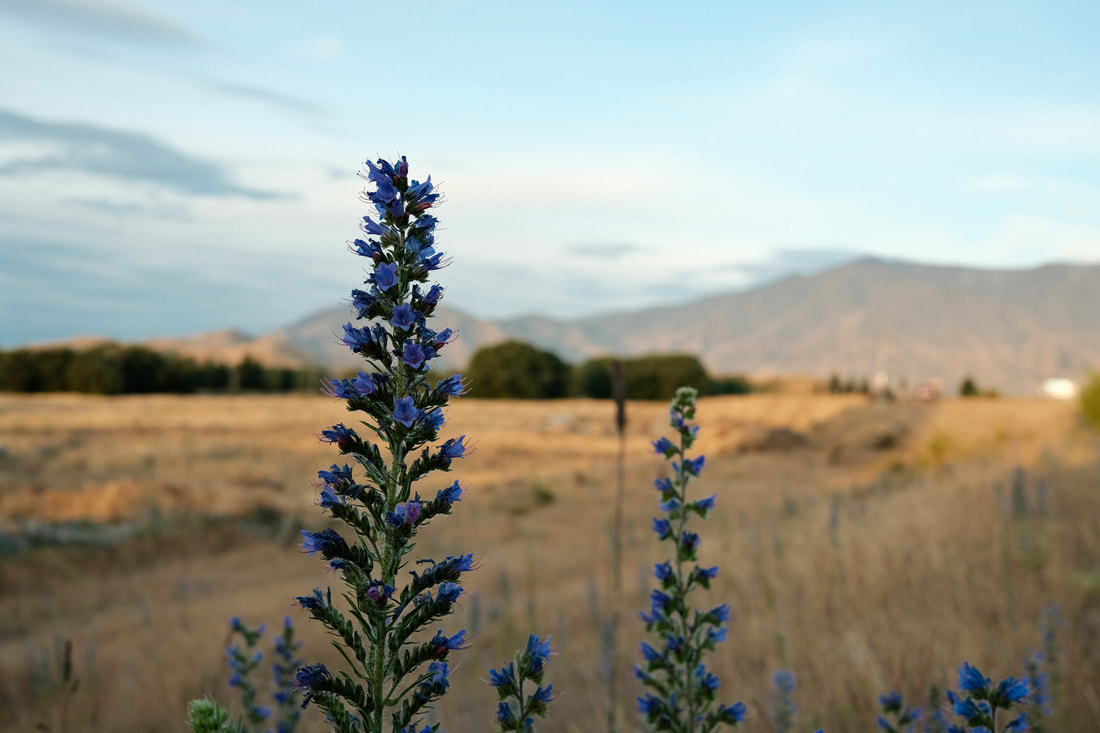
Recently, I announced the findings of empirical research conducted over an eight year period. The aim of that research was to discover how many boards are fully aligned in relation to corporate purpose. The findings were staggering: five per cent of the participating boards—yes, one in twenty—were completely aligned in relation to corporate purpose. When asked, every director and executive had an answer, but only five boards (out of one hundred and three, to date) had one answer. How can any board do its job (make informed decisions, and provide effective steerage and guidance) if it has not first agreed on an objective (purpose) to work towards? Compare this situation with that of a plant. The example in the picture—echium vulgare, or, more commonly, viper's bugloss or blueweed—is as good as any. Echium vulgare, a native of Europe, is an introduced species in parts of north-eastern North America, south-eastern South America, and New Zealand. The plant is toxic to horses and cattle, but the bright blue flowers are very attractive to bees. And, despite the toxins in the plant, honey produced from the nectar is very tasty indeed! "So what?" you might ask. To compare a board and a plant seems a little odd. Yes, maybe, but please allow me to explain. E. vulgare, like all other plants, has a single purpose, which is to grow and reproduce. All the plant's energies are dedicated to this single goal, using the resources available to it. Nothing more, and nothing less. In contrast, many companies operate without an overarching and enduring goal, as the research mentioned above shows (save to make a profit). And that begs another question: how can any organisation realise its full potential without first establishing a clearly defined and achievable goal? 'Purpose' has become a hot topic in board, shareholder and stakeholder circles. Some have interpreted purpose to mean mission and vision: an overarching goal the company intends to achieve. Others have a different understanding—one that positions the company as a servant of society, as the question below illustrates: How can a company not be in the business of improving human health and making the world a better place? This question, posed by a US-based leadership consultant, positions purpose as a catalyst to influence or resolve an external societal or environmental situation. In effect, the underlying expectation is that the company prioritises something external and, most probably, well beyond the company's means and ability to influence, much less achieve. The difference between the two understandings is stark, as are the implications. Readers will, probably, gravitate towards one or other, and some may hold such strong views as to be offended by 'the other one'. And that is okay; shareholders and the board can strive to achieve whatever they want—such is their prerogative. What matters is that every board takes responsibility for answering the question, of why the company it is charged with governing exists. Essentially, "For what purpose?" Without this, the company will lack a North Star, and efforts to create a meaningful strategy, let alone allocate resources well and achieve high levels of performance, will be fraught. But, if purpose is clearly stated, and agreed and understood by every director and all key staff, the company will not only attain membership of a most desirable club—the Five Percent Club—the board will have established a robust foundation upon which a coherent strategy can be developed, resources allocated, decisions made, and the full potential of the company pursued. And that, I think, is a good thing.
3 Comments
|
SearchMusingsThoughts on corporate governance, strategy and boardcraft; our place in the world; and other topics that catch my attention. Categories
All
Archives
May 2024
|
|
Dr. Peter Crow, CMInstD
|
© Copyright 2001-2024 | Terms of use & privacy
|